Introduction
Medical transport devices, such as vacuum stretchers and splints, are crucial for safe and efficient patient transport in hospitals, ambulances, and other medical settings. Unlike rigid spine boards, these devices mold precisely to the patient’s body, offering both immobilization and comfort. They reduce the risk of injury during transport. This is why the use of vacuum stretchers has become a standard practice in medical transport.
This comprehensive guide will explore how vacuum stretchers work, when to use them, key differences from traditional boards, and what to look for when choosing a vacuum mattress for your rescue kit. Whether you’re an EMS provider, hospital buyer, or safety officer, this article will help you make informed decision.
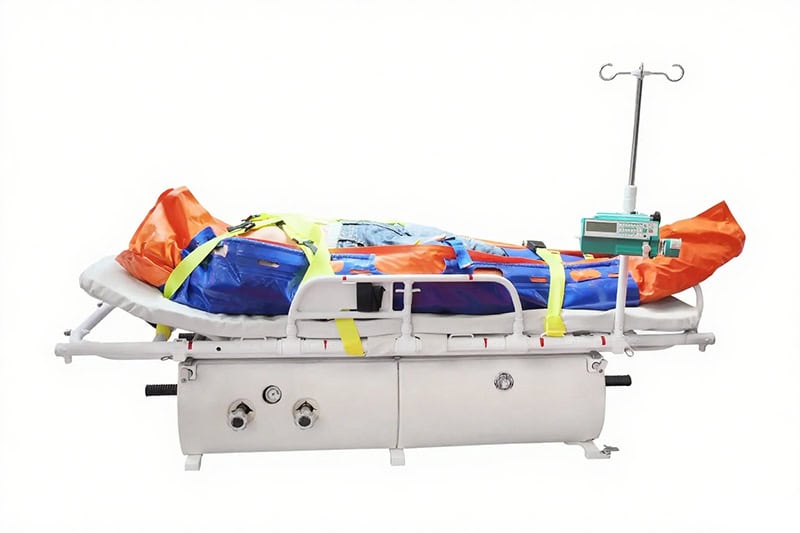
What is Vacuum Mattress and Vacuum Splint?
Vacuum stretchers and splints are advanced medical devices used to immobilize patients during trauma care. They are made up of tiny beads inside a flexible outer shell. Once placed around the injured area, the air is pumped out and the splint hardens into a rigid, supportive mold, creating a customized support system. Vacuum splints are typically used for individual limb injuries like fractures or dislocations, while vacuum stretchers (also called vacuum mattresses) are full-body devices used for spinal trauma. Their ability to combine comfort with stability makes them an essential piece in modern emergency and rescue settings.
Vacuum stretchers are used when spinal, pelvic, or multiple limb injuries are suspected. They provide an alternative to the rigid spine board and are especially useful for longer transports, rough terrain rescues, and pediatric or bariatric patients.
How to Pump Air for Immobilization
Vacuum splints use a simple but highly effective technique:
- The splint is filled with polystyrene beads.
- Once wrapped around the injured area, a pump removes the air.
- As air exits, the beads compress and the splint hardens around the body part.
- The result is a custom rigid support that limits motion during transport.
How Vacuum Splints Help in Patient Transport
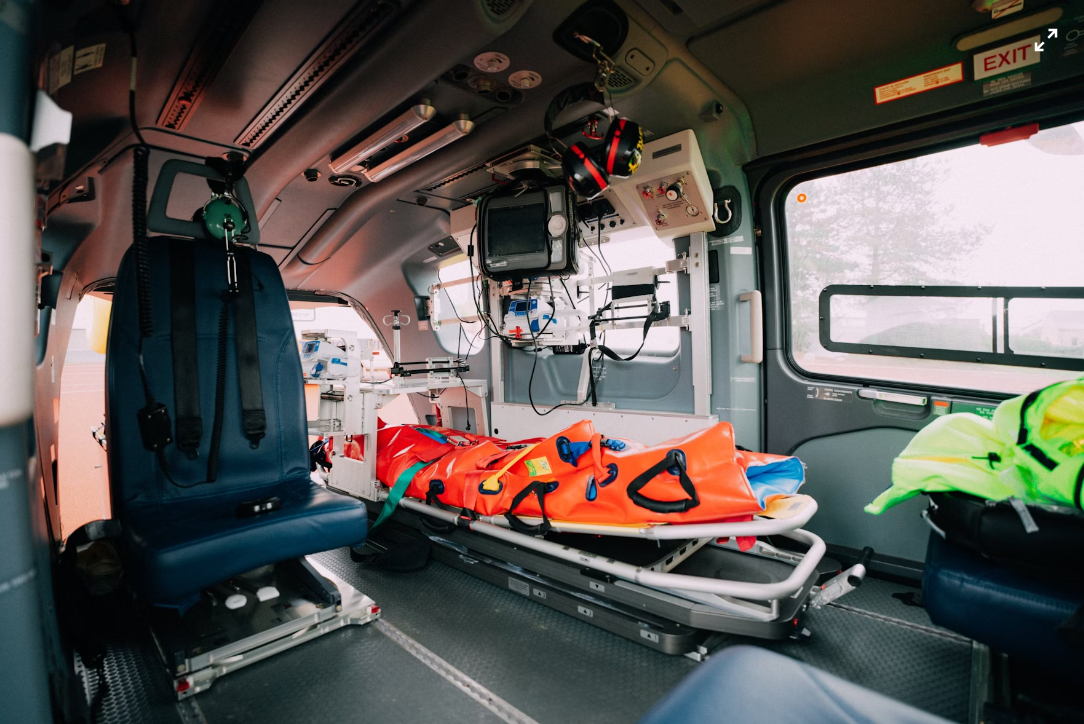

Vacuum splints are crucial to protect patients during transport, especially in trauma cases where even slight movement can worsen injuries. By molding precisely to the injured limb or body part, these splints minimize motion, reduce pain, and lower the risk of further damage during transfer. Their importance lies in how they combine physical support, patient comfort, and transport stability during emergencies.
1. Minimize Patient Movement
During transport, even a slight movement of a fractured bone, dislocated joint, or spinal segment can worsen the injury or lead to complications. Vacuum splints conform exactly to the patient’s body, locking the injured part in place and eliminating internal shifting. This reduces pain and prevents further damage during loading, unloading, and ambulance motion.
2. Adjustable to Any Terrain
Whether rescuing someone from a mountain slope, confined space, or accident scene, vacuum stretchers can be used in any environment. Their flexibility makes them far more adaptable than flat boards, allowing for safer extraction.
3. Patient Comfort Over long Distances
Unlike rigid boards or metal splints, vacuum splints distribute pressure evenly and mold to natural body shape. This makes them ideal for long ambulance rides, airlifts, or transport over rough terrain, scenarios where standard boards may cause discomfort, numbness, or even pressure ulcers.
4. Suitable for Pediatric and Bariatric Transport
Vacuum splints and stretchers come in multiple sizes, including pediatric and bariatric models. This adaptability ensures proper immobilization for vulnerable populations who often don’t fit securely on standard spine boards.
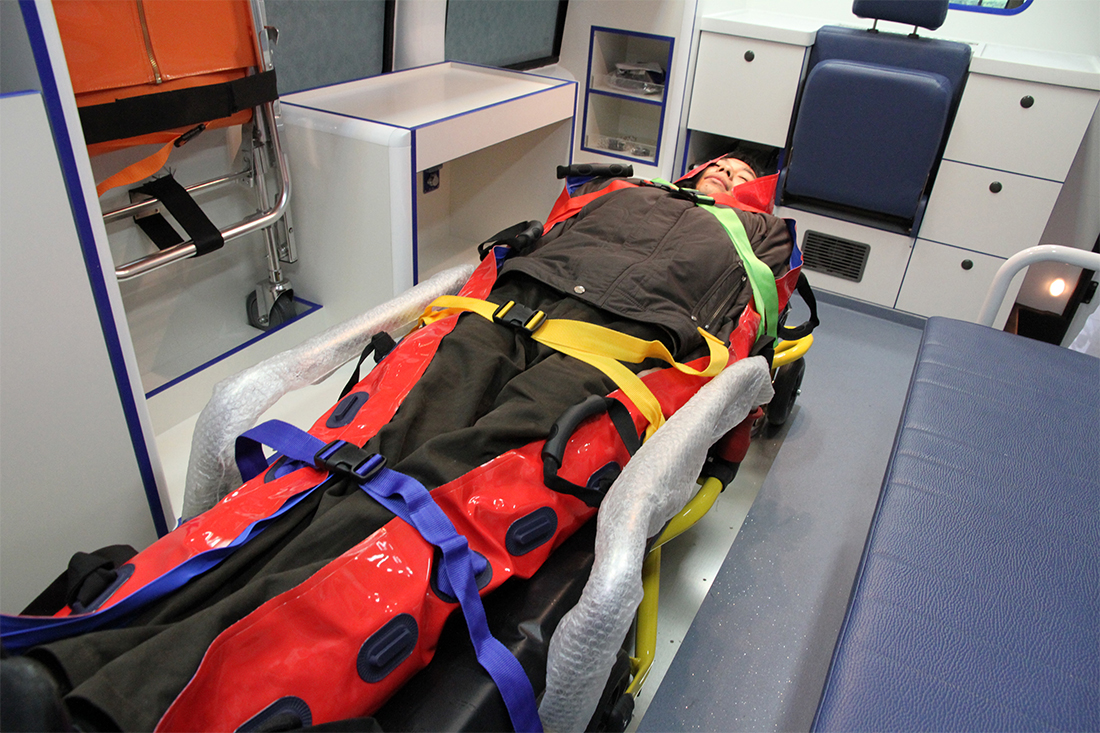
5. Portable and Easy to Use
Vacuum stretchers are designed to be lightweight and compact size, making them ideal for ambulance, airlift, or field rescue scenarios. The use of a vacuum pump and adjustable straps can make it easy to set up and use the device.
Jiekang offers multiple resuce stretcher options for cutomised patient needs. Available on the link.
Specifications Comparison (Top Brands)
| Model | Dimensions (L × W) | Weight | Material |
|---|---|---|---|
| EVAC-U-SPLINT Fulal Body | 210 × 90 cm | ~9 kg | Vinyl + polystyrene beads |
| Hartwell FASPLINT Limb Kit | Variable (30–100 cm) | 0.5–2.2 kg | Nylon laminate + beads |
Buying Guide: Choosing the Right Vacuum Mattress or Splint
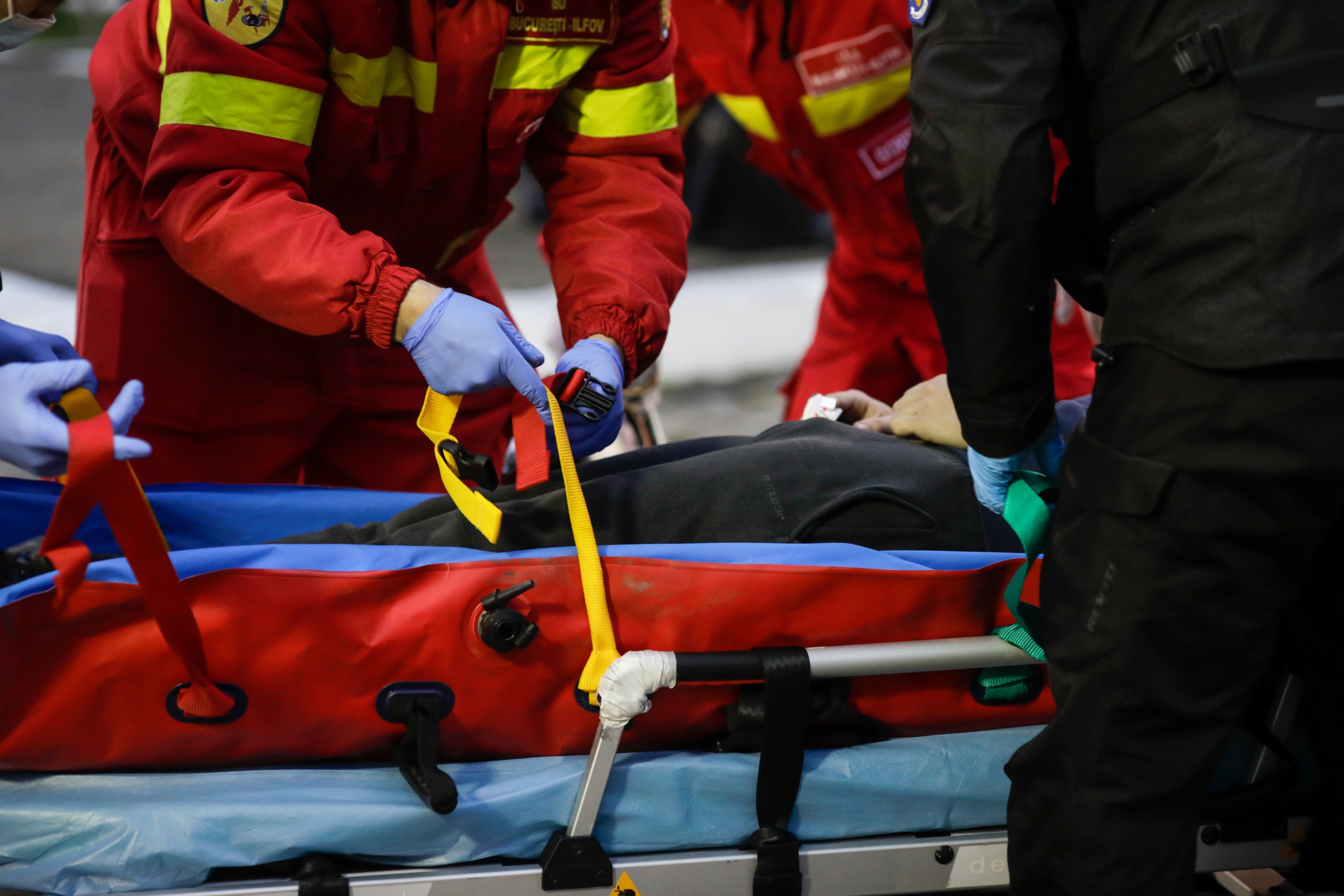

When choosing an immobilization device, healthcare professionals should consider several factors, including the patient’s condition, the medical setting, and the device’s features.
Here’s what to consider when purchasing:
- Purpose: Limb or Full-Body ImmobilizationLimb Splints are ideal for isolated fractures (arms, legs, shoulder). While Vacuum Mattresses or full-body stretchers are essential for spinal, pelvic, or multiple trauma injuries which need full-body stabilization.
- Dimensions: Vacuum devices come in a range of sizes:a. Standard full-body vacuum mattress: ~210 cm (L) × 85–90 cm (W)b. Pediatric models: ~120–150 cm longc. Limb splints: Typically 30 cm to 100 cm in length
- Weight and Portability: Weight varies from 0.5 kg for limb splints to 9–10 kg for full-body mattresses. If your rescue scenarios involve long distance, lighter models with compact folding capacity are preferable.
- Material Durability & Cleaning: The manufacturing material of vacuum stretcher matters a lot.PE or PVC-coated nylon: high abrasion resistance and easy to disinfectDouble-sealed seams for long-lasting airtight performanceWaterproof and washable surfaces for hygiene between uses
- Valve & Pump Quality: The valve system controls air evacuation speed and seal quality: Mechanic Vacuum valve: Offers fast air removal and prevents leaksManual hand pump vs built-in suction: Manual pumps are more portable, while built-in or foot pumps are better for fast setup.
- Certifications: Always verify that your vacuum device is: CE-certified FDA-approved (for U.S. buyers) Compliant with ISO standards.
- Price Range: Vacuum splints typically range from $60 to $400, depending on their size, material quality, included accessories and brand certification. A slightly higher upfront price often pays off with longer lifespan and better field performance.
By carefully evaluating these factors, healthcare professionals can select the best immobilization device for their patients’ needs. If you need expert guidance in this matter, Jiekang can help you with that. Reach out to our professioanals for their advice.
How to Use a Vacuum Splint (5-Step Guide)
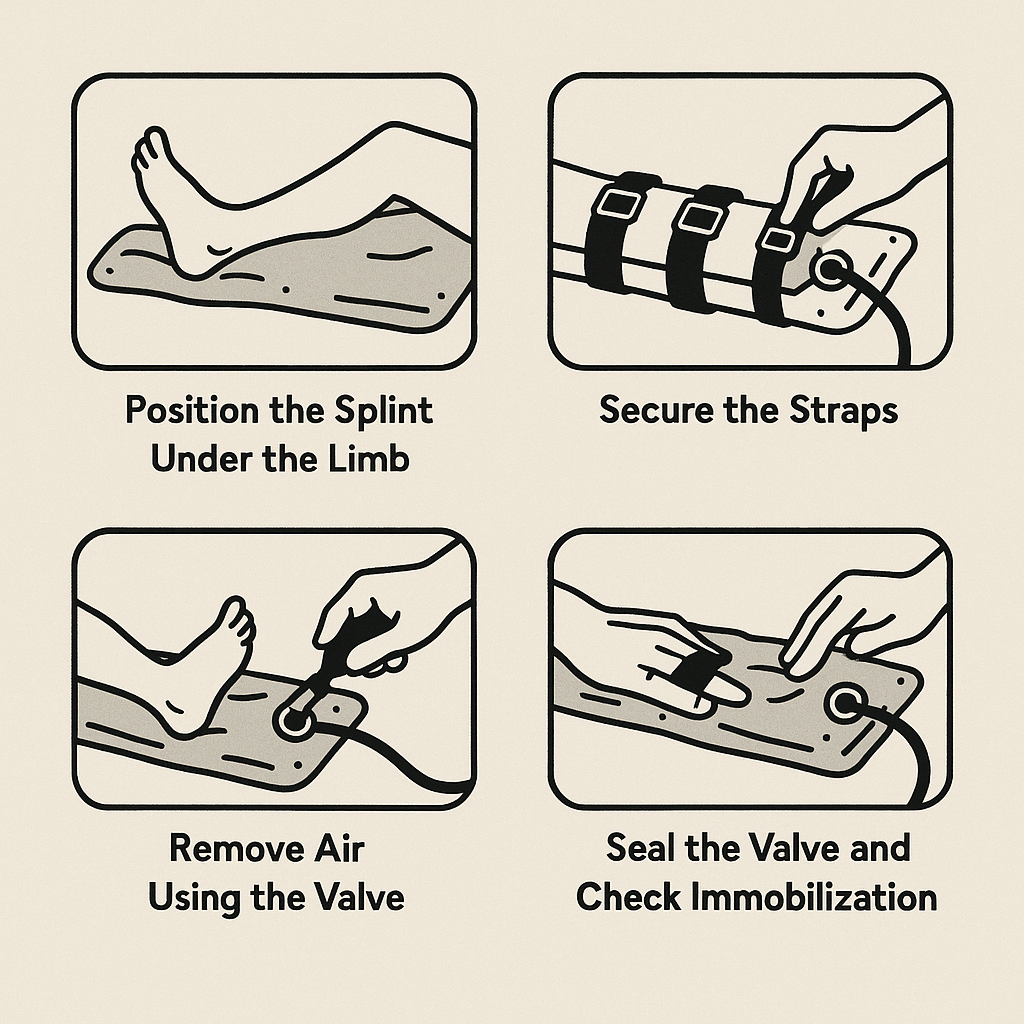
Vacuum splints provide custom-molded immobilization, and applying them correctly is extremely important. The following 5-step guide is referenced from the official Hartwell Medical FASPLINT Application Manual (2024):
Step 1: Position the Splint Under the Limb
Lay the vacuum splint flat and place it beneath the injured limb. While sliding the limb on the splint, ensure that the splint extends above and below the joints to fully immobilize the fracture site.
Step 2: Secure the Straps
Before suction, loosely fasten the attached straps or securing bands to maintain the splint’s shape around the injury.
Step 3: Remove Air Using the Valve
Attach the manual or electric pump to the valve and begin removing air from the splint. As air is removed, the internal beads lock into place, conforming to the patient’s anatomy. Continue until the splint becomes rigid.
Step 4: Seal the Valve and Check Immobilization
Once the splint is firm, remove the pump and close the valve to prevent air from re-entering. Gently press around the splint to verify coverage of the injury.
Step 5: Recheck Straps and Circulation
Tighten the straps fully for secure immobilization. Then check for distal circulation: confirm the presence of a pulse, sensation, and movement beyond the splint. Adjust as necessary.
This process takes about 2–5 minutes, depending on the model and experience of the responder.
Necessary Requirements for Effective Use of Vacuum Sprints
Vacuum splints are only as effective as the way they’re used. To ensure proper immobilization, both human and technical factors must be addressed. These include training, equipment readiness, and routine maintenance.
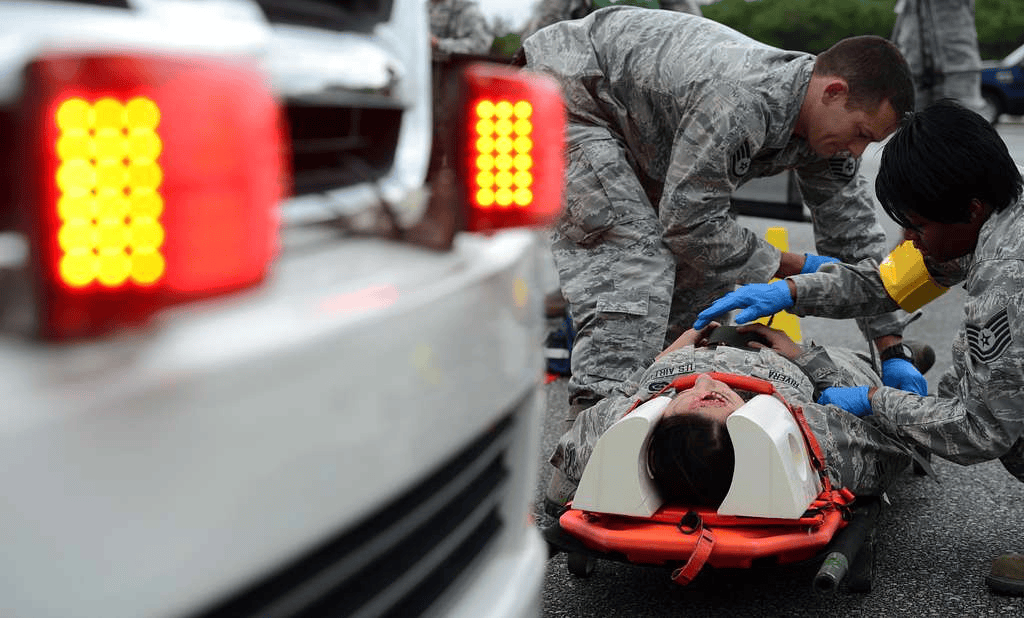

Proper Personnel Training
EMS personnel, nurses, and trauma responders should receive:
- Hands-on training in selecting the correct size and position
- Practice with air evacuation and valve operation
- Drills for pediatric and bariatric patients
- Reinforcement of protocols, such as checking distal pulses and reassessing tightness after application
Training should be refreshed annually or in accordance with regional EMS standards.
Routine Inspection and Maintenance
To keep vacuum splints field-ready:
- Inspect the outer shell for punctures, tears, or material fatigue
- Check valve seals and gaskets for leaks
- Test the pump function (manual or electric) regularly
- Ensure straps are intact and Velcro fasteners grip securely
- Store in a clean, dry location to prevent mold or valve corrosion
Most manufacturers recommend routine inflation-deflation checks and full functionality tests monthly or after each use.

Availability of Supporting Equipment
Teams should ensure:
- A working pump is always attached or stored with the splint
- Spare valves or repair kits are stocked
- Appropriate sizing options (S, M, L) are on hand for limb injuries
Storage and Readiness
In high-stress emergencies, access and readiness are everything. Splints should be:
- Make sure the vacuum pump is kept free of dust and debris. Wipe it down with a dry cloth.
- Store the stretcher in a clean, dry area when not in use. Avoid excess moisture. Avoid exposing the stretcher to extreme hot or cold temperatures in storage.
- Clearly labeled and stored in an organized trauma bag
- Folded compactly to save space but easily retrievable
- Placed near stretchers or airway equipment in ambulances or ER carts
Cleaning Vacuum Splints
After each use, vacuum splints should be wiped down with a soft cloth and a mild detergent solution to remove blood, dirt, or bodily fluids. Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive scrubbing, as they can damage the outer shell or valve system. Allow the splint to air dry completely before storage to prevent mold or material degradation. Regular cleaning ensures hygiene and extends the product’s lifespan.
Conclusion
Vacuum splints and stretchers have revolutionized pre-hospital care by offering personalized immobilization, enhanced comfort, and safer patient transport. Whether you’re treating isolated limb fractures or managing full-body spinal trauma, choosing the right vacuum device and applying it correctly can make a life-saving difference. With this guide, you will better understand the vacuum splints, stretchers and mattresses in order to make the right decision. You can also explore high-quality stretchers and other rescue boards at Jiekang.